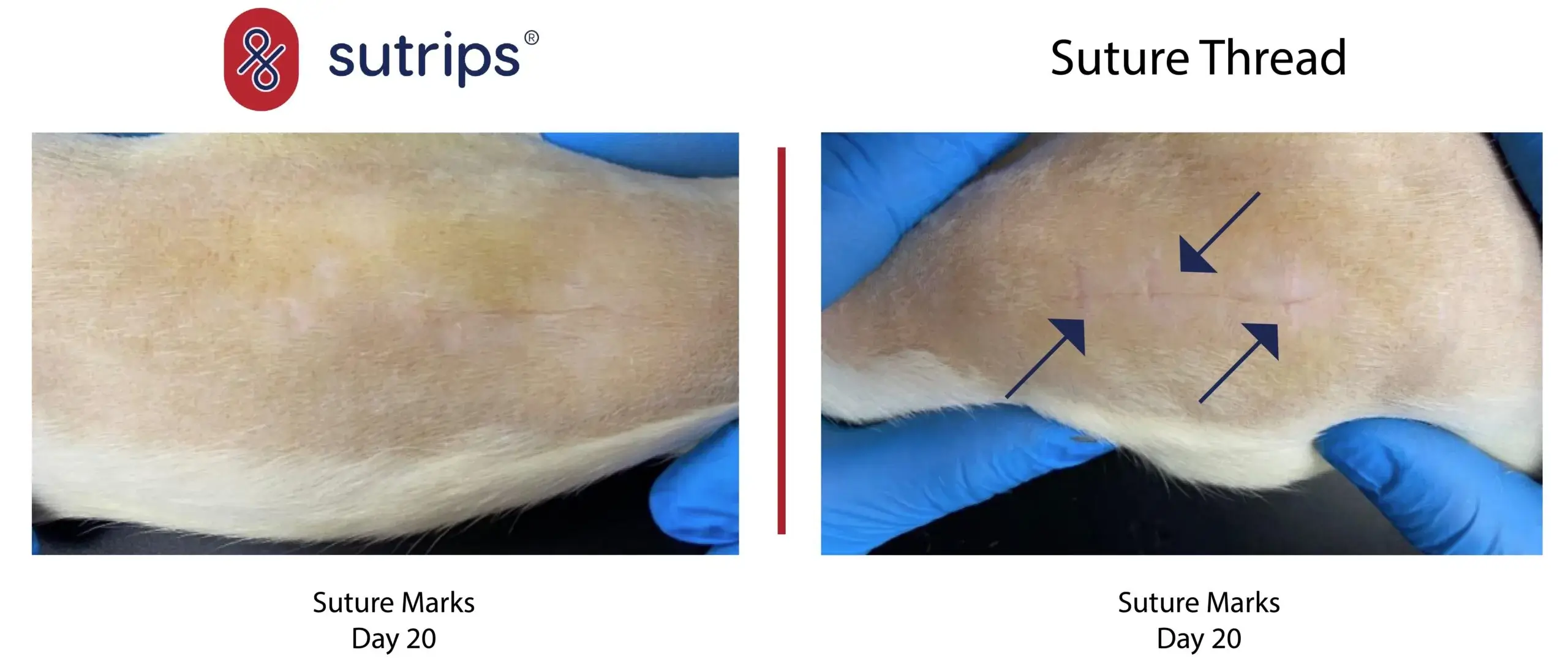
Suture Marks: A Persistent Challenge in 2023
By Ubbat Ocak Posted November 1, 2023
Suture Marks: A Persistent Challenge in 2023
In 2023, the persistence of suture marks on the skin remains a subject of interest and inquiry. To address this concern, we must first understand the nature and origins of suture marks and explore potential avenues for their prevention and reduction. One such avenue is Sutrips®, an innovative wound closure device from MUB Medical Solutions. Before delving further into this topic, we invite you to follow MUB Medical Solutions AS for updates and news.
To commence our exploration of suture marks, it is essential to grasp the concept of wound closure through ‘primary intention.’ This process involves the meticulous alignment of wound edges, achieved through various means, including stitches, adhesive strips, staples, or glue. The primary objective is to eliminate interstitial spaces within the wound, ensuring optimal healing. Gaps between tissues can lead to complications such as infection and wound dehiscence.
Additionally, precise stitching aims to minimize the formation of conspicuous scars. This entails careful alignment of the upper skin layers to prevent raised or sunken scar formation, ultimately enhancing the cosmetic outcome of the procedure.
The choice of wound closure method depends on factors such as the wound’s location, size, proximity to vital structures, the surgeon’s expertise, and the cause of the injury. The overarching goal is to achieve secure closure with minimal tension, promoting optimal healing and a pleasing cosmetic result (Gillies H.).
Excessive tension during wound closure, characterized by tight approximation of wound edges, can yield adverse consequences. It may impede blood supply, resulting in hypoxia, causing skin breakdown, loss of color, and the development of visible scars (Field L.).
Many different suture techniques exist. The most common is the simple interrupted stitch. It is indeed the simplest to perform and is called “interrupted” because the suture thread is cut between each individual stitch (Shokrollahi et al). Like interrupted stitches or running stitches, can cause problems if they are too tight, as the thin thread can press into the skin and create issues like erosion or ulcers. The vertical and horizontal mattress stitch are also interrupted but are more complex and specialized for everting the skin and distributing tension, but these techniques need experience, knowledge, and it’s a time-consuming process.
Alternative wound closure techniques, including suture-less methods such as isoamyl-2-cyanoacrylate and adhesive strips, have been proposed to mitigate suture marks. Nonetheless, these techniques may pose challenges for irregular, bleeding, or deep wounds.
Sutrips®, an innovative suture technique, revolutionizes wound closure by eliminating the common issue of vertical suture marks associated with traditional methods. Sutrips® expertly align wound edges beneath the skin’s surface, eliminating filament pressure on the skin, thus preventing microvascular compression. This novel technique ensures the absence of visible vertical suture marks, as demonstrated in the headline picture.
In summary, suture marks remain a concern in 2023, influenced by a multitude of factors. Precise wound closure and the avoidance of excessive tension are paramount for optimal healing and minimal scarring. Advancements in medical knowledge continue to enhance our ability to achieve improved outcomes in wound closure and suture mark reduction. Sutrips® represents a promising and groundbreaking approach. Stay updated on our progress. Follow us at MUB Medical Solutions AS .
READ MORE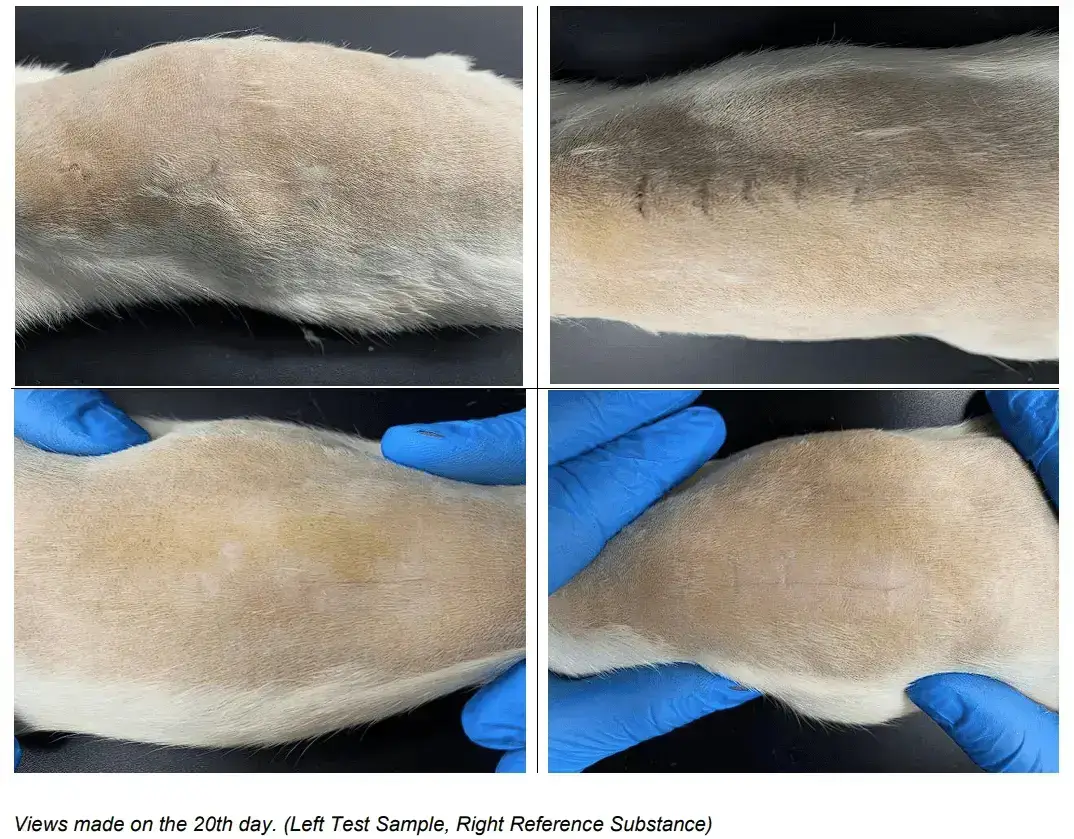
Recent Comments